Counting the number of breaths
Counting the number of breaths
The functional state of the respiratory and cardiovascular systems will be determined by counting the number of respiratory movements in the patient. Indications for counting the frequency of respiratory movements are mainly diseases of the respiratory system and the cardiovascular system. Before considering the sequence of actions of this manipulation, let us recall what breathing is in general.
Breathing is the main life process that provides a continuous supply of oxygen to the body and the release of carbon dioxide and water vapor from the body. There are the following types of breathing in humans, depending on the involvement of the chest in the process.
Thoracic type of breathing
With a chest type of breathing in a person, the chest expands mainly in the anteroposterior and lateral directions. This type of breathing is more common in women. In this case, the lower parts of the lungs may not be sufficiently ventilated.
Abdominal type of breathing
In the abdominal type of breathing in humans, the expansion of the chest cavity occurs mainly due to the diaphragm in the vertical direction. This type of breathing is more typical for men. In this case, the tops of the lungs may be insufficiently ventilated.
Mixed type of breathing
With a mixed type of breathing, a uniform expansion of the chest cavity occurs in all directions, which ensures sufficient ventilation of all parts of the lungs.
Normally, the frequency of respiratory movements (RR) in an adult is 16-20 per 1 minute. In newborns, the normal respiratory rate is 40-60 per minute, in children 1-2 years old - 30-40.
Counting the number of breaths
You will need a stopwatch to count. It is not necessary to inform the patient about counting his respiratory movements, because in this case the patient will begin to control his breathing, which will distort the true picture of the study.
The sequence of actions of a nurse
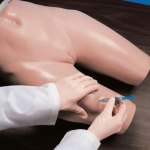
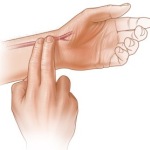
- In the patient's lying position, we take his hand as for counting the pulse and, together with our hand, put it on the front surface of the patient's chest.
- According to the excursions of the chest or abdominal wall, we count the number of respiratory movements in 1 minute, while counting either inhalations or exhalations.
- We register the result in the patient's temperature sheet, graphically recording the results and displaying the breathing curve. The curve is obtained by connecting the points, with the date or time marked horizontally, and the NPV marked vertically.
Counting the number of respiratory movements plays a significant role in assessing the patient's condition (improvement or deterioration, or lack of dynamics).